# VueRouter原理及实现
VueRouter中主要有2种路由模式,history模式和hash模式,俩种模式都是客户端的变化,不会像服务器发送请求
- hash路由中url中会带有一个#号,#号后面的才是路由地址,基于锚点以及onhashchange事件
- history模式是基于H5中的history API,监听popstate事件(浏览器的前进和后退,router的back和forward事件才会触发popstate)
history.pushState()不会向服务器端发送请求,只会改变浏览器中的地址并生成历史记录history.replaceState()
# 实现分析
在Vue中,使用VueRouter的方式,如下
// vue的main.js
// 创建Vue实例,注册Router对象
new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
// router/index.js
// 导入VueRouter
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// 注册插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routers: [
{ name: 'home', path: '/', component: HomeComponent }
]
})
- 在Vue中,
Vue.use方法传入的可以是一个函数或者是对象,如果是一个函数,use内部会直接调用这个函数,如果是一个对象,use会调用这个对象中的install方法。 - VueRouter是一个构造函数/类,传入的参数是一个对象
- VueRouter类中需要实现的方法
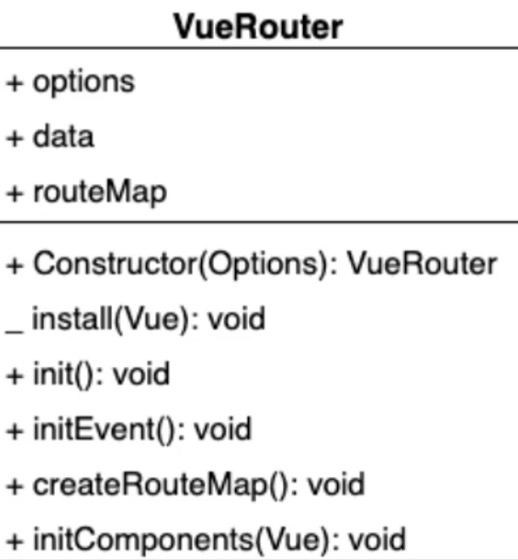
# 实现install方法
install(Vue) {
// 1. 判断当前插件是否被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) {
return
}
VueRouter.install.installed = true
// 2. 把Vue构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue
// 3. 把创建Vue实例时候传入的router对象注入到Vue实例上
// 使用Vue实例中的混入,来实现给Vue实例挂载$router对象
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// Vue实例中存在router对象才进行挂载, 组件实例不挂载$router
if (this.$options.router) {
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
}
}
})
}
# 实现VueRouter构造函数
constructor(options) {
this.options = options
this.routerMap = {}
// data是一个响应式的对象 Vue.observable()
// 也可以使用Vue提供的utils包中的definReactive方法
// Vue.util.defineReactive(this, 'current', '/');
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/'
})
}
# 实现createRouteMap方法和initComponents方法
// createRouteMap 主要 遍历传入的路由规则,把路由规则解析成key-value的形式,存到routeMap中
createRouteMap() {
this.options.routes.forEach(route => {
this.routerMap[route.path] = route.component
})
}
// initComponents 主要实现router-link router-view组件
// 这里使用Vue.component方法给Vue实例注册router-link、router-view组件
// 这里创建组件的时候不能使用template模板, 因为在vue-cli中使用的是运行时版本的Vue,是没有编译器将template模板编译成vDom
// 所以只能使用render函数
// 或者修改vue-cli中配置,将使用运行版本的Vue改成带有编译器的运行时Vue版本
// 在vue-config.js中修改runtimeCompiler: true即可
initComponents(Vue) {
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: String
},
// template: '<a :href="to"><slot></slot></a>'
// Vue实例会传入一个h函数
render(h) {
return h(
'a', // a标签
{ attrs: { href: this.to } }, // a标签的href属性 history模式 this.to,hash模式 `#${this.to}`
[this.$slots.default] // slot插槽
)
}
})
// router-view组件
const self = this
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
// 通过 this.data.current 获取当前路由地址
// 在通过routerMap中找到对应地址的路由组件
// 最后通过h函数将路由组件转成vDom并返回
const comp = self.routerMap[self.data.current]
return h(comp)
}
})
}
# 完整代码
仅实现了history模式路由
// 定义一个全局变量存储Vue实例
let _Vue = null
class VueRouter {
static install(Vue) {
// 1. 判断当前插件是否被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) {
return
}
VueRouter.install.installed = true
// 2. 把Vue构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue
// 3. 把创建Vue实例时候传入的router对象注入到Vue实例上
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// Vue实例中存在router对象才进行挂载, 组件实例不挂载$router
if (this.$options.router) {
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
// 调用初始化
this.$options.router.init()
}
}
})
}
// 构造函数
constructor(options) {
this.options = options
this.routerMap = {}
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/'
})
}
init() {
this.createRouteMap()
this.initComponents(_Vue)
}
// createRouteMap
createRouteMap() {
this.options.routes.forEach(route => {
this.routerMap[route.path] = route.component
})
}
// initComponents
initComponents(Vue) {
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: String
},
render(h) {
return h(
'a',
{
attrs: { href: this.to },
on: {
click: this.clickHandler
}
},
[this.$slots.default]
)
},
methods: {
clickHandler(e) {
history.pushState({}, '', this.to)
this.$router.data.current = this.to
e.preventDefault()
}
}
})
const self = this
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
const comp = self.routerMap[self.data.current]
return h(comp)
}
})
}
}
← Vue.nextTick原理 Vue3原理 →